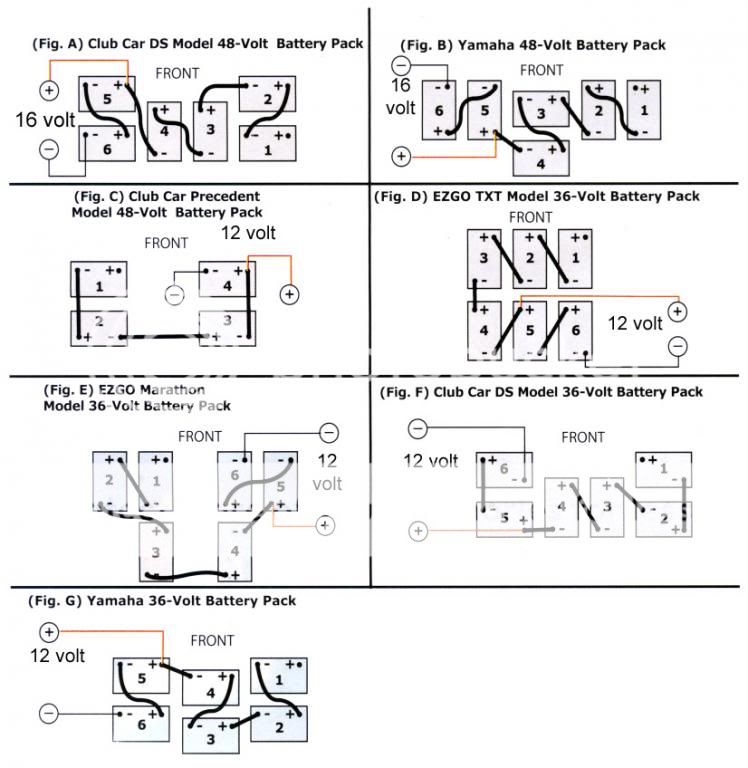
When it comes to understanding the electrical system of your 48-volt battery meter, having a wiring diagram can be extremely helpful. A 48 Volt Battery Meter Wiring Diagram is a visual representation of the connections and layout of the various components in the system. This diagram is essential for anyone looking to install, troubleshoot, or repair their battery meter system.
Why are 48 Volt Battery Meter Wiring Diagrams essential?
- Helps you understand the layout of the system
- Aids in identifying and connecting the various components
- Ensures proper installation and functioning of the battery meter
- Allows for easy troubleshooting and repairs
How to read and interpret 48 Volt Battery Meter Wiring Diagrams effectively
Reading a wiring diagram may seem overwhelming at first, but with a little guidance, it can become much easier. Here are some tips to help you read and interpret a 48 Volt Battery Meter Wiring Diagram:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the symbols used in the diagram
- Identify the power source, ground, and other key components
- Follow the flow of the diagram to understand how the components are connected
- Pay attention to color codes and labels for easier interpretation
Using 48 Volt Battery Meter Wiring Diagrams for troubleshooting electrical problems
Wiring diagrams are invaluable tools when it comes to troubleshooting electrical issues in your battery meter system. Here’s how you can use a wiring diagram for troubleshooting:
- Identify the specific area where the issue is occurring
- Trace the connections in the diagram to pinpoint any potential wiring faults
- Check for loose connections, damaged wires, or faulty components
- Refer to the diagram to ensure correct reconnection of any disconnected wires
Importance of safety when working with electrical systems
When working with electrical systems and wiring diagrams, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Always turn off the power source before working on any electrical components
- Use insulated tools to prevent electric shock
- Avoid working in wet or damp conditions to reduce the risk of electric shock
- Double-check all connections before powering up the system to prevent short circuits
48 Volt Battery Meter Wiring Diagram
48v battery meter wiring diagram – pennyqust

Solar DC Battery Wiring Configuration | 48v Design and Instructions for

Battery Wiring Diagram for 48 Volt Golf Cart [Complete Guide]
![48 Volt Battery Meter Wiring Diagram Battery Wiring Diagram for 48 Volt Golf Cart [Complete Guide]](https://i1.wp.com/thefunoutdoors.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Battery-Wiring-Diagrams-For-48-Volt-Golf-Carts-1.jpg)
Club car wiring diagram 48 volt

Club Car Precedent 48 Volt Battery Wiring Diagram » Wiring Digital And

48 Volt Golf Cart Battery Meter Wiring Diagram Database